Gastroenterology is the branch of medicine that focuses on the health of the digestive system, also known as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. This vital system is responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste, playing a central role in overall health and well-being. In this blog, we’ll dive into the world of gastroenterology, the common conditions it addresses, and tips for maintaining a healthy digestive system.
What Is Gastroenterology?
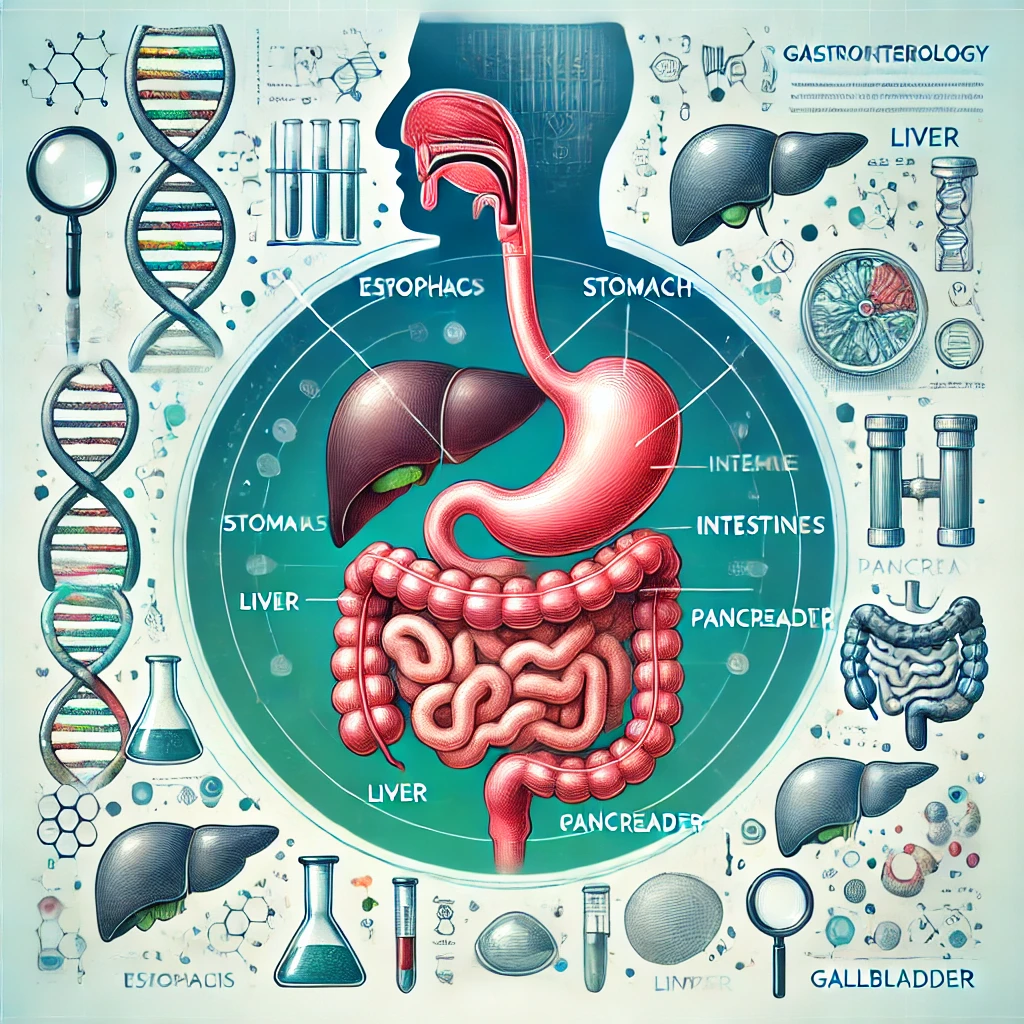
Gastroenterology deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disorders affecting the stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and esophagus. A gastroenterologist is a physician specializing in these organs and is equipped to manage a wide range of digestive issues, from heartburn to more complex conditions like Crohn’s disease or liver disorders.
Key Organs of the Gastrointestinal Tract
The digestive system is a complex network that includes:
- Esophagus: Transports food and liquids from the mouth to the stomach.
- Stomach: Breaks down food with digestive enzymes and acids.
- Small Intestine: Absorbs nutrients from digested food.
- Large Intestine (Colon): Processes waste and absorbs water.
- Liver: Produces bile to aid in fat digestion and processes toxins.
- Pancreas: Produces digestive enzymes and insulin to regulate blood sugar.
- Gallbladder: Stores bile and releases it during digestion.
Common Gastrointestinal Conditions
Gastroenterologists treat a variety of conditions, including:
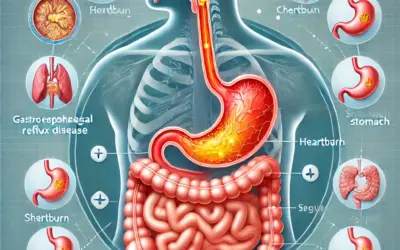
1. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing heartburn, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing. Left untreated, GERD can lead to complications such as esophagitis or Barrett’s esophagus.
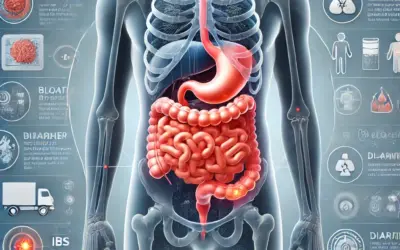
2. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
IBS is a functional GI disorder that causes symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, or constipation. It’s a chronic condition often triggered by stress, diet, or hormonal changes.
3. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
IBD includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, which cause chronic inflammation in the GI tract. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue.
4. Hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver, often caused by viral infections (Hepatitis A, B, or C), alcohol use, or autoimmune conditions. It can lead to liver damage or failure if untreated.
5. Gallstones
Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that form in the gallbladder. They can cause severe pain, nausea, and digestive issues, often requiring surgical removal.
6. Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is an autoimmune condition triggered by gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. Eating gluten causes inflammation in the small intestine, leading to nutrient malabsorption and digestive symptoms.
7. Colon Cancer
Colon cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide, but it is highly treatable when detected early. Routine screening, such as a colonoscopy, can help identify precancerous polyps before they develop into cancer.
Symptoms That Require a Gastroenterologist
If you experience any of the following symptoms, it may be time to consult a gastroenterologist:
- Persistent abdominal pain or discomfort
- Chronic diarrhea or constipation
- Blood in the stool or black, tarry stools
- Heartburn or acid reflux that doesn’t improve with over-the-counter treatments
- Unexplained weight loss
- Difficulty swallowing
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes)
Diagnostic Tools in Gastroenterology
Gastroenterologists use advanced diagnostic techniques to identify and treat GI conditions. Common procedures include:
- Colonoscopy: A procedure to examine the colon and rectum for polyps, inflammation, or cancer.
- Endoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a camera is used to examine the esophagus, stomach, and upper intestines.
- Liver Function Tests: Blood tests to assess liver health and detect hepatitis or liver disease.
- Imaging Studies: Techniques like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs to evaluate organs like the pancreas, gallbladder, or liver.
- Biopsies: Tissue samples taken during procedures to diagnose conditions like celiac disease or cancer.
Tips for a Healthy Digestive System
Maintaining a healthy GI system is key to overall well-being. Here are some tips to support your digestive health:
1. Eat a Balanced Diet
- Include plenty of fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes to support regular bowel movements.
- Limit processed foods, high-fat meals, and sugary snacks that can disrupt digestion.
- Stay hydrated, as water is essential for breaking down food and absorbing nutrients.
2. Practice Portion Control
Eating large meals can overwhelm the digestive system. Instead, opt for smaller, frequent meals to prevent bloating or indigestion.
3. Stay Active
Regular exercise promotes healthy digestion by improving gut motility and reducing stress.
4. Manage Stress
Stress can have a direct impact on your digestive health, contributing to conditions like IBS. Practice mindfulness, meditation, or deep breathing to reduce stress levels.
5. Avoid Smoking and Excess Alcohol
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can damage the digestive tract and increase the risk of conditions like GERD or liver disease.
6. Get Screened Regularly
Routine screenings like colonoscopies can help detect GI issues early, improving treatment outcomes.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While occasional digestive discomfort is normal, persistent or severe symptoms may indicate an underlying issue. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to preventing complications and improving quality of life.
Conclusion
Gastroenterology plays a vital role in understanding and managing the complexities of the digestive system. From diagnosing common conditions like acid reflux to addressing chronic illnesses such as Crohn’s disease, gastroenterologists help patients maintain optimal digestive health. By adopting healthy habits, staying informed, and seeking timely medical care, you can ensure that your GI system remains in peak condition for years to come.